Nanomedicine & Targeted Therapies
Precision therapies using nanoparticles for liver imaging, neural drug delivery, and diagnostics, advancing personalized medicine
Nanomedicine is reshaping how we visualize disease, deliver drugs to protected or difficult-to-reach tissues, and convert molecular signals into actionable clinical decisions. At its core, it leverages nano‑scale carriers and contrast agents engineered for high specificity, controlled payload release, imageability, and safety. In hepatic and neuro‑therapeutics, this translates into earlier detection of pathology, minimally invasive targeted interventions, and individualized care pathways that respond to a patient’s molecular profile and real‑time disease dynamics. Our center’s translational lineage from hepatocyte transplantation and human hepatic progenitor cell (HPC) therapy to bioengineered neo‑organs and imageable nanoparticle platforms provides an integrated bench‑to‑bedside capability that is rare in the region.
Why nanomedicine for the liver and the brain
Diseases of the liver and central nervous system (CNS) pose distinct barriers: the liver’s fenestrated vasculature and complex detox pathways can rapidly sequester or deactivate drugs, while the blood–brain barrier (BBB) excludes most therapeutics from entering neural tissue. Nanocarriers overcome these hurdles through tunable size, surface charge, ligand decoration, and stimuli‑responsive chemistries that enhance hepatic tropism or enable receptor‑mediated transcytosis across the BBB. Our progression from clinical hepatocyte and hepatic progenitor cell therapies in fulminant liver failure, Crigler–Najjar syndrome, biliary atresia, and advanced cirrhosis to precision, image‑guided nano‑interventions gives us a full spectrum view of how to pair the right platform with the right patient at the right time.
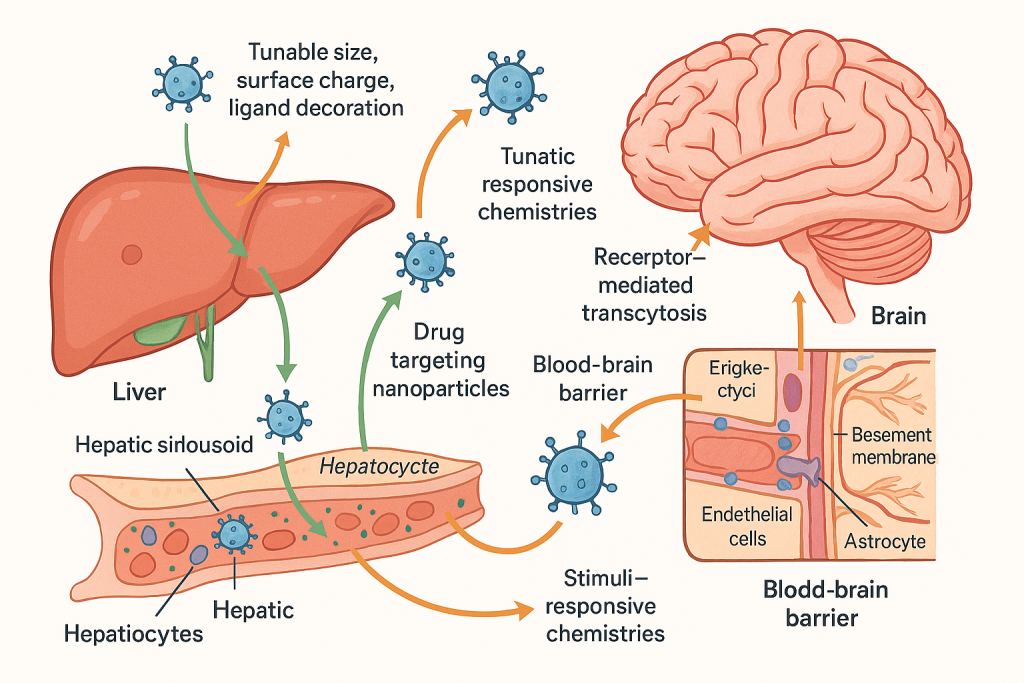
Precision liver imaging with nano‑contrast systems
Accurate, high‑contrast hepatic imaging is foundational for staging disease, planning interventions, and monitoring therapeutic response. Superparamagnetic iron oxide–gadolinium composite nanoconstructs synthesized and validated for dual MRI contrast in our program demonstrate high biocompatibility and robust T1/T2 signal modulation, enabling lesion conspicuity at lower doses than conventional agents. These FeGdO3 nano‑platforms, developed by our nanomaterials team, allow molecular imaging workflows that co‑register perfusion, fibrosis progression, and tumor microenvironment dynamics, setting the stage for truly image‑guided therapy.
For oncology, we exploit theranostic nanoconjugates that combine a drug and an imaging handle within a single vehicle. Sorafenib–gold nanoconjugates pioneered within our group reverse resistance in human hepatoblastoma models while maintaining real‑time optical and electron density signatures that facilitate response tracking and dose‑refinement; similarly, bimetallic redox nanoprobes augment hyperthermia efficacy and permit live‑cell tracking of uptake and intracellular trafficking. These capabilities map directly onto clinical objectives such as shrinking the time from radiologic progression to regimen switch, or escalating local therapy only where drug‑resistant niches are detected.
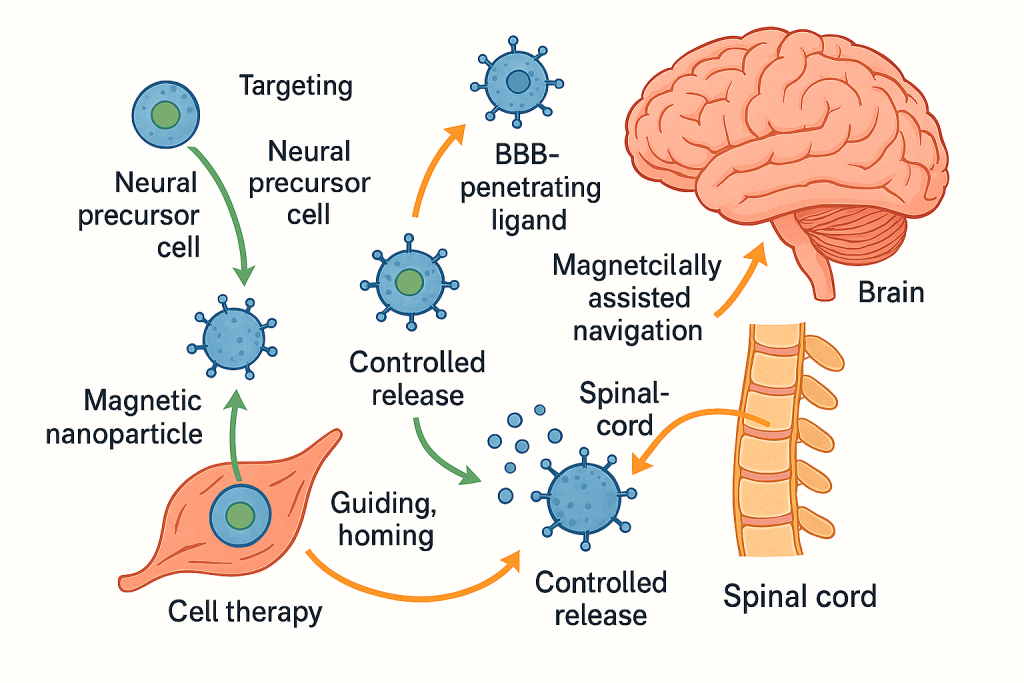
Targeted neural drug delivery that crosses the BBB
Delivering neuroprotective or disease‑modifying agents to the brain remains a pivotal challenge. Building on our long‑standing neural stem cell (NSC) and neural precursor cell platforms, we deploy nano‑enabled strategies to improve targeting, retention, and controlled release in CNS injury and neurodegeneration. Magnetic nanoparticle tagging has been used to guide and home cell therapies to spinal cord lesions, a principle we now extend to payload‑bearing nanocarriers functionalized with BBB‑penetrating ligands and magnetically assisted navigation. This approach integrates with our rigor in NSC isolation, characterization, and transplantation, as well as our programmatic work on heat‑shock proteins, transporters, and hypothermia synergies allowing us to couple cellular and nano‑formulations where appropriate or use nano‑only regimens when cell therapy is not indicated.
Our safety framework for neural delivery draws on extensive in‑vitro stress‑response mapping in human neural precursor cells and ethanol‑injury models, informing surface chemistry selection, dosing bands, and release kinetics to minimize neuroinflammation while maximizing target engagement.
Diagnostic nanotechnologies and companion decisioning
Precision medicine depends on precise diagnostics. Our ecosystem supports nanoparticle‑enabled detection and molecular companion tests that can be run on small volumes of blood, saliva, or tissue. We have validated rapid genotyping and PCR‑free colorimetric platforms for viral RNA detection, refined multiplex biopsy and saliva‑based assays for pathogenic virulence signatures, and advanced circulating nucleic acid analytics, including simultaneous extraction and quantification of mitochondrial and nuclear cell‑free DNA from a single plasma sample. These assets integrate well with nano‑imaging and nano‑therapeutic programs to create closed‑loop “diagnose–treat–monitor–adapt” cycles.
For inflammatory and septic pathologies, our teams have profiled immune meta‑signatures, mitochondrial DAMPs, and endothelial dysfunction biomarkers, knowledge that directly informs the design of inflammation‑attenuating surface coatings and the timing of nano‑interventions in critically ill patients. This molecular insight supports risk stratification and toxicity mitigation before and during nano‑based therapies.
Treatment specialization: how we individualize nano‑enabled care
We operate a treatment architecture that begins with molecular mapping, proceeds to image‑guided delivery, and adapts therapy based on dynamic biomarkers. In hepatic oncology and advanced chronic liver disease, we select from a menu of nano‑platforms, drug–metal nanoconjugates for chemoresistance, dual‑mode MRI agents for guidance, and heat‑triggered or redox‑responsive nanocarriers for microenvironment‑specific release. Where regenerative support is needed, we integrate hepatic progenitor cell infusions or bioengineered humanized liver grafts that we have shown can support failing livers in acute settings, now increasingly paired with exosome‑rich, cell‑free products from humanized neo‑livers to amplify paracrine repair while avoiding immunosuppression.
In neural indications, our specialization focuses on spinal cord injury and neurodegenerative contexts where targeted delivery can amplify the benefit of NSCs or replace them when cellular therapy is contraindicated. We leverage magnetically assisted homing, thermally modulated release, and transporter‑aware formulations derived from our gene‑expression work on ABC transporters and molecular chaperones in human neural precursor cells. This allows us to tailor cargo, carrier, and control signals to a patient’s transporter profile and inflammatory set‑point, improving penetration and persistence at the lesion.
Safety, biocompatibility, and translational stewardship
Patient safety underpins every nano‑intervention. Our nanomaterials library includes soft‑chemistry‑synthesized metal‑oxide platforms and noble‑metal constructs vetted through iterative biocompatibility screens in human hepatic and neural cells, hemocompatibility assays for gold nanoparticles, and hepatocytotoxicity safeguards for emerging oxides. The same teams that delivered the region’s early hepatocyte and hepatic progenitor cell transplants bring a disciplined clinical mindset to first‑in‑human translation, dose‑finding, and adverse‑event surveillance. This continuum materials science to regulated bedside delivery has been exercised repeatedly across liver support, spinal injury, and cancer nano‑programs.
CLRD capability in diagnosis and treatment
Our Center for Liver & Regenerative Disorders (CLRD) integrates nanotechnology, cellular therapy, organ bioengineering, and molecular diagnostics into a unified clinical service line for liver and select neuro indications. In diagnosis, we deploy dual‑contrast MRI nanoprobes for sensitive lesion detection and perfusion mapping, saliva‑ and tissue‑based molecular genotyping panels for oncogenic and infectious drivers, and plasma cell‑free DNA assays to monitor disease activity and therapeutic impact. These diagnostics are paired with real‑time image‑guided nano‑therapies and are supported by a decision layer that incorporates endothelial and immune biomarkers in critically ill patients to calibrate timing and intensity of intervention. This approach shortens time‑to‑diagnosis, enables earlier and more targeted treatments, and allows rapid pivoting when resistance or progression is detected.
In treatment, our specialization spans: liver‑directed theranostics—sorafenib–gold nanoconjugates and bimetallic redox nanoprobes for drug‑resistant hepatobiliary tumors under image guidance; regenerative adjuncts hepatic progenitor cell infusions and bioengineered humanized liver grafts for acute and chronic failure, complemented by therapeutic exosomes to promote repair; neural targeting magnetically navigable nanoparticles and NSC co‑therapies designed around transporter and stress‑response biology; and critical‑care interfaces nano‑enabled strategies that are timed and tuned using our sepsis and endothelial dysfunction biomarker panels. Each pathway is protocolized but remains individualized through companion diagnostics and on‑treatment molecular readouts.
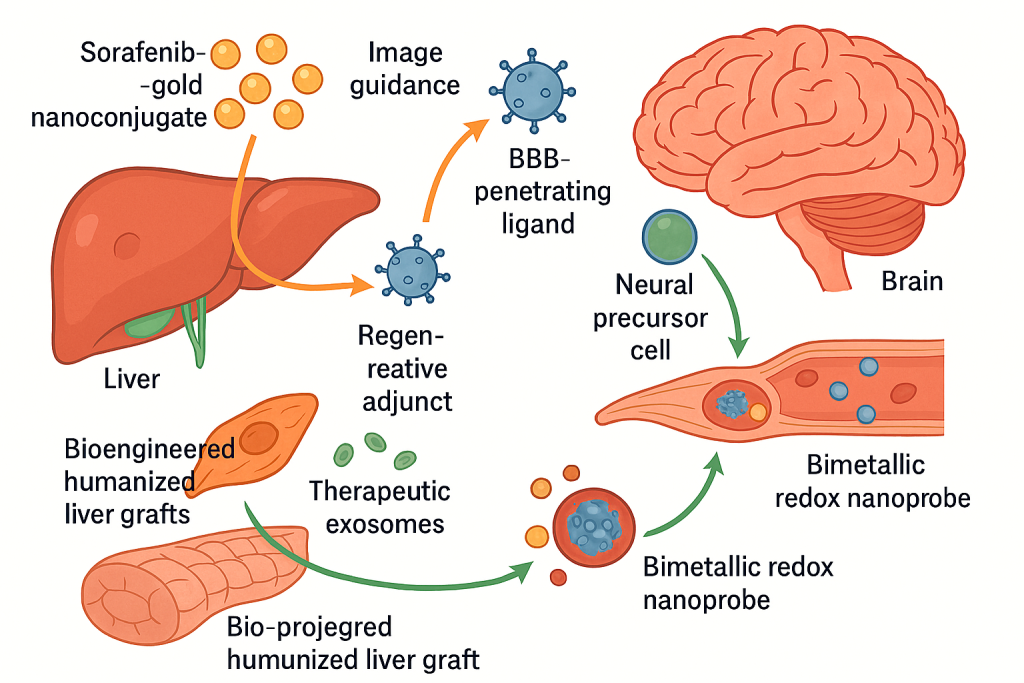
A typical patient journey under our nanomedicine program
Patients begin with a molecular–radiologic baseline built from advanced MRI using dual‑mode nano‑contrast, plasma cfDNA and mitochondrial DNA quantification, and disease‑specific genotyping or virulence profiling when indicated. A tumor exhibiting chemoresistance, for example, might be assigned a sorafenib gold nanoconjugate protocol with hyperthermia augmentation where bimetallic nanoprobes both sensitize the lesion and allow intra‑procedural monitoring. In parallel, liver‑function trends and inflammatory indices are tracked. If decompensation risk emerges, we layer in hepatic progenitor cell support or implant a bioengineered auxiliary graft for bridging, then de‑escalate once parenchymal recovery is evident. In neural care, we assess BBB permeability surrogates and transporter signatures to select a BBB‑crossing nanocarrier, optionally combining it with magnetically guided NSCs; intra‑patient parameters such as heat‑shock responses influence release‑profile settings and cooling adjuncts. The plan adapts at predefined checkpoints based on imaging signal changes, cfDNA kinetics, and biomarker panels, with safety gates triggered by endothelial injury markers in the ICU setting.
What sets our treatment specialization apart
Our nanomedicine is not a stand‑alone experiment; it is embedded in a mature translational framework that has already delivered clinical hepatocyte and progenitor cell therapies, including peritoneal and intra‑arterial routes, and demonstrated in‑vivo support with bioengineered humanized livers. Add to this our validated nano‑contrast agents for MRI, drug‑nanoconjugates that overcome resistance, magnetic homing strategies, and rapid molecular assays, and you have a continuum capable of diagnosing, treating, and adaptively managing complex hepatic and neural diseases with precision. This depth materials to molecules to mechanisms to medicine is the essence of CLRD’s capability in both diagnosis and treatment.
