HLA Typing and Immune Profiling
At CLRD, advanced immunogenetic and molecular technologies converge to deliver personalized care for complex conditions. Our approach integrates high-resolution HLA typing, comprehensive immune profiling, and transcriptomic analysis to stratify disease risk, guide therapy selection, and optimize transplant outcomes. This capability stems from decades of CLRD’s pioneering research, now translated into clinical workflows that improve patient survival and quality of life.
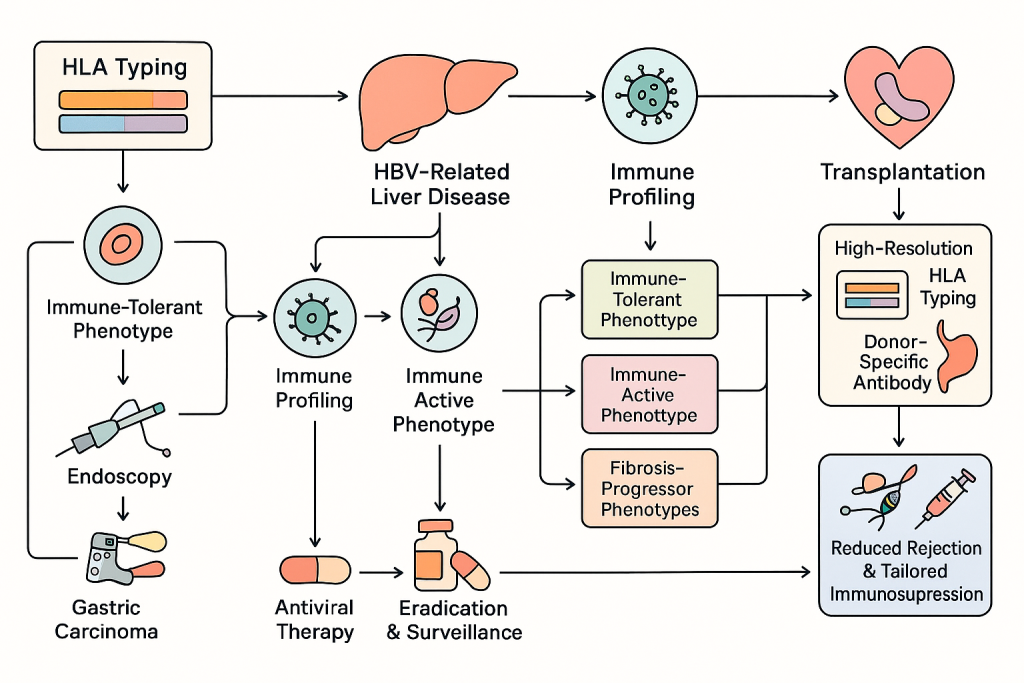
HLA Typing: Linking Genetic Risk to Clinical Decisions
HLA typing is central to understanding individual susceptibility to HBV-related liver disease and gastric carcinoma. CLRD’s early investigations demonstrated that specific HLA antigen frequencies correlate with hepatitis B surface antigen status and gastric cancer risk. Today, these insights inform our diagnostic algorithms. In HBV clinics, HLA typing combined with viral markers and immune activation profiles predicts disease progression, identifies candidates for immune-tolerant or immune-active strategies, and supports transplant readiness. In gastric carcinoma prevention programs, HLA-DR antigen profiling complements Helicobacter pylori virulence genotyping to guide eradication therapy and surveillance intensity. For transplantation, high-resolution HLA typing and donor-specific antibody screening reduce rejection risk and enable tailored immunosuppression.
Clinical Workflow and Protocol:
Patients with HBV undergo baseline evaluation including HBsAg, HBeAg, HBV DNA quantification, liver stiffness measurement, and HLA typing. Immune profiling follows to determine inflammatory status. Based on these results, patients are categorized into immune-tolerant, immune-active, or fibrosis-progressor phenotypes. Antiviral therapy is initiated according to phenotype, and transplant readiness is assessed for advanced disease. For gastric cancer risk, patients presenting with dyspepsia or premalignant lesions undergo endoscopy, biopsy, HLA typing, and H. pylori genotyping. Eradication regimens are selected based on virulence and resistance profiles, and high-risk individuals are enrolled in intensified surveillance programs.
Advanced Immune Profiling: Decoding Immune Dysregulation
CLRD’s immune profiling platform captures cellular and soluble immune signatures that drive autoimmune disorders, inflammatory bowel disease, and chronic liver inflammation. We analyze T-cell subsets, NK cell activity, cytokine circuits, and markers of immune exhaustion alongside circulating immune complexes, autoantibodies, and neutrophil extracellular traps. These data allow us to map dominant inflammatory pathways and select targeted therapies. For example, patients with IL-23/Th17 signatures benefit from IL-23 or IL-17 inhibitors, while TNF-driven phenotypes respond to anti-TNF agents. In HBV, immune profiling distinguishes cytolytic from immune-tolerant states, guiding antiviral timing and immunomodulation. In transplant settings, dynamic immune monitoring informs early detection of rejection and infection, enabling precise immunosuppressive adjustments.
Clinical Workflow and Protocol:
For autoimmune and IBD patients, initial assessment includes colonoscopy, biopsy, and serology, followed by immune profiling to identify dominant pathways. Transcriptomic analysis is added for refractory cases. Therapy selection is based on pathway dominance, with biologics or JAK inhibitors prescribed accordingly. Monitoring involves biomarker remission targets such as CRP and fecal calprotectin, with repeat immune profiling every 12 weeks. HBV patients receive immune profiling at baseline and during antiviral therapy to predict flares and adjust treatment. Transplant recipients undergo immune profiling immediately post-surgery and at scheduled intervals to detect early rejection or infection.
Transcriptome Analysis: From Molecular Signature to Therapy
Beyond conventional biomarkers, CLRD employs transcriptome analysis to reveal pathway-level insights. RNA sequencing of blood or tissue samples identifies cytokine networks, RNA-binding protein signatures, and stress-response pathways such as JAK-STAT and NF-κB activation. These findings influence therapy sequencing in IBD and autoimmune conditions, predict flare risk, and support oncology decisions by characterizing tumor immune microenvironments. For patients with refractory disease, transcriptomic data often uncover actionable targets that standard panels miss, ensuring that treatment remains adaptive and evidence-based.
Clinical Workflow and Protocol:
Transcriptome analysis is performed for patients with complex or treatment-resistant disease. Samples are processed using next-generation sequencing, and results are interpreted by a multidisciplinary team. Reports include pathway activation profiles and therapeutic recommendations. Follow-up testing is scheduled every six months or upon clinical relapse to refine treatment strategies.
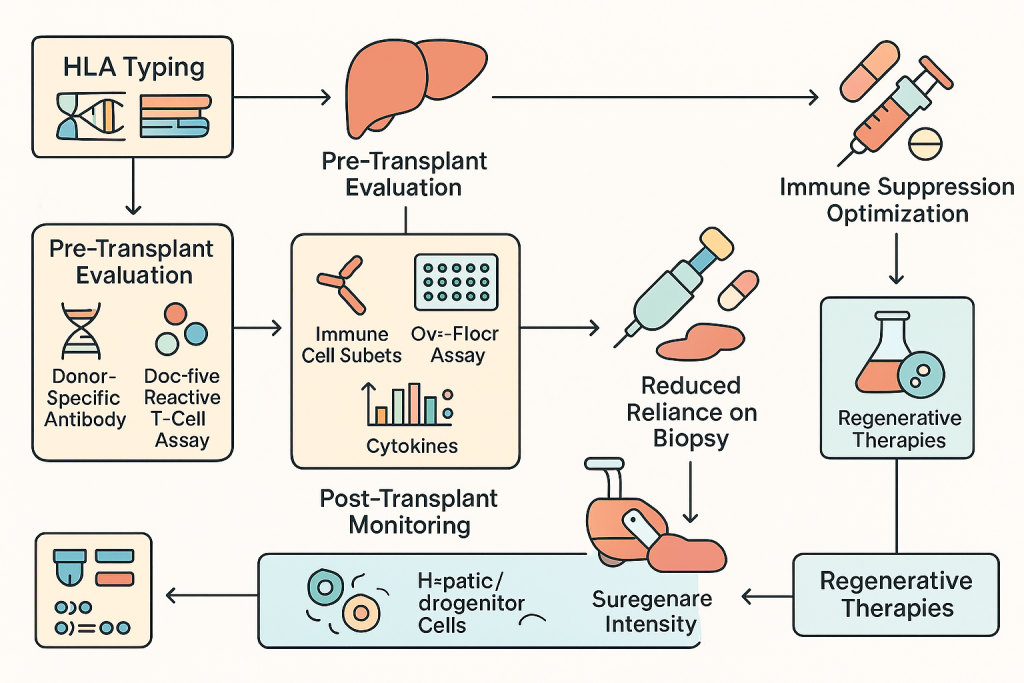
Cellular Immune Studies in Transplantation: Enhancing Graft Survival
Transplant immunology at CLRD combines genetic and functional assessments to minimize rejection. Pre-transplant evaluation includes HLA typing, donor-specific antibody detection, and donor-reactive T-cell assays. Post-transplant, we monitor immune cell subsets, cytokine trends, and non-invasive markers such as cell-free mitochondrial DNA and exosomal injury signals. These strategies reduce reliance on biopsies and allow real-time immunosuppression optimization. CLRD’s expertise extends to regenerative therapies, including hepatocyte and hepatic progenitor cell transplantation for acute and chronic liver failure. Our protocols incorporate immune tolerance strategies developed through years of cellular therapy research.
Clinical Workflow and Protocol:
Before transplantation, patients undergo comprehensive immunogenetic screening, including HLA typing and crossmatch testing. Functional assays such as ELISPOT are performed to assess donor-reactive T-cell activity. Immunosuppressive regimens are personalized based on these findings. Post-transplant monitoring includes serial immune profiling and non-invasive biomarkers to detect rejection early. In regenerative therapy programs, patients receive hepatocyte or hepatic progenitor cell infusions under strict GMP conditions, with immune monitoring protocols adapted from transplant experience.
Integrated Care Pathways and Monitoring
Each program at CLRD follows a structured care pathway. HBV patients progress from diagnostic evaluation to risk stratification, therapy initiation, and longitudinal monitoring. IBD patients move from immune and transcriptomic profiling to targeted biologic therapy and treat-to-target remission strategies. Gastric cancer prevention integrates molecular diagnostics with eradication therapy and surveillance. Transplant and regenerative therapy pathways emphasize pre-procedure immune risk assessment, personalized immunosuppression, and continuous immune monitoring. All pathways are supported by digital tools for remote follow-up and patient engagement.
CLRD’s Diagnostic and Therapeutic Capabilities
Our service portfolio includes high-resolution HLA typing, immune profiling panels for autoimmune and inflammatory conditions, transcriptomic diagnostics for precision therapy, and cellular immunology services for transplant compatibility. These capabilities are complemented by regenerative medicine programs offering hepatocyte and hepatic stem cell transplantation as bridge or alternative strategies for end-stage liver disease. Each intervention is supported by CLRD’s multidisciplinary team and governed by strict quality protocols to ensure safety and efficacy.
Why CLRD?
CLRD stands apart for its ability to translate research into practice. Our published work on HLA-disease associations, immune signatures in IBD and rheumatoid arthritis, Helicobacter pylori virulence diagnostics, and cellular immune responses in transplantation forms the backbone of our clinical programs. This scientific depth ensures that every diagnostic report and treatment plan reflects the latest evidence and decades of institutional expertise. Patients and referring physicians benefit from personalized care pathways, rapid turnaround times, and integrated monitoring systems designed to achieve durable remission, prevent complications, and optimize transplant outcomes.
